Docker Compose update on Github webhook
Learn how to update Docker Compose on push to Github using webhooks
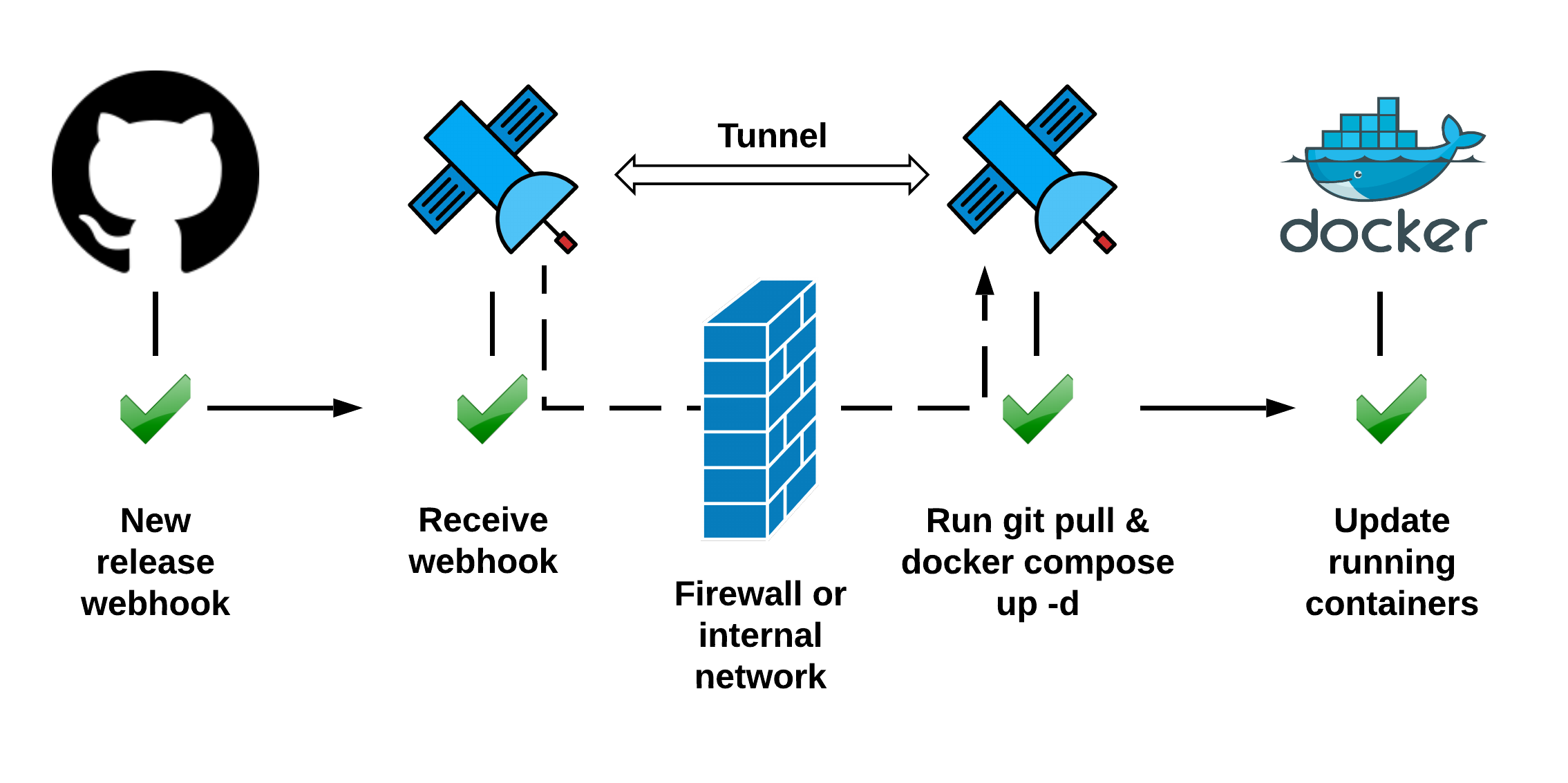
Last year I wrote a blog post about combining several tools to automate simple NodeJS app updates on git push. Many users were solving similar problems by writing local web servers in Ruby, Python or PHP to receive webhooks and to do the update. I am happy to announce that we have decided to add this feature to the relay client. Now, to execute a bash script, you can:
relay forward --bucket my-bucket-name --relayer exec --command bash update.sh
And to launch a Python app on webhook:
relay forward --bucket my-bucket-name --relayer exec --command python my-app.py
This opens up some interesting possibilities to create pipelines that can react to pretty much anything that emits webhooks. In this article I will show you how to build a GitOps style pipeline that does Docker Compose update to sync with a docker-compose.yaml hosted on a git repository.
Prerequisites
- Docker & Docker Compose
- Webhook Relay account with configured relay CLI
- Github account
Repository with scripts that I used for this article can be found here: https://github.com/webhookrelay/docker-compose-update-on-git-push.
Step 1: Deploying containers through Docker Compose
First step is to do the initial deployment. We will create a simple dockerized Python application that you can find here that connects to Redis and deploy it:
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: "karolisr/python-counter:0.1.0"
ports:
- "5000:5000"
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
Step 2: Setting up updates on Github tag
Since we only want to update on git tags and not just any pushes, let's configure a webhook and analyze the payload.
To achieve that, let's first create a bucket with an internal output:
$ relay forward --bucket docker-compose-update-on-git-push http://localhost:4000
Forwarding:
https://my.webhookrelay.com/v1/webhooks/a956a9f7-2260-4bc2-a54b-3d896acf4206 -> http://localhost:4000
Starting webhook relay agent...
2019-08-28 23:14:41.773 INFO using standard transport...
2019-08-28 23:14:41.928 INFO webhook relay ready... {"host": "my.webhookrelay.com:8080", "buckets": ["8e977e70-09a6-464c-ad30-855e1cd5d9f9"]}
Here, bucket will be used later to subscribe to github requests while destination is just a mandatory argument that we don't have to use in this case.
Grab that https://my.webhookrelay.com/v1/webhooks/*** URL and go to your repository's settings -> webhooks section. Once there, set:
- Payload URL to your unique https://my.webhookrelay.com/v1/webhooks/*** URL
- Content type to application/json
- Secret to a random secret name, for the sake of this example my secret will be 'webhooksecret'
- Click
Let me select individual events.and select Releases.
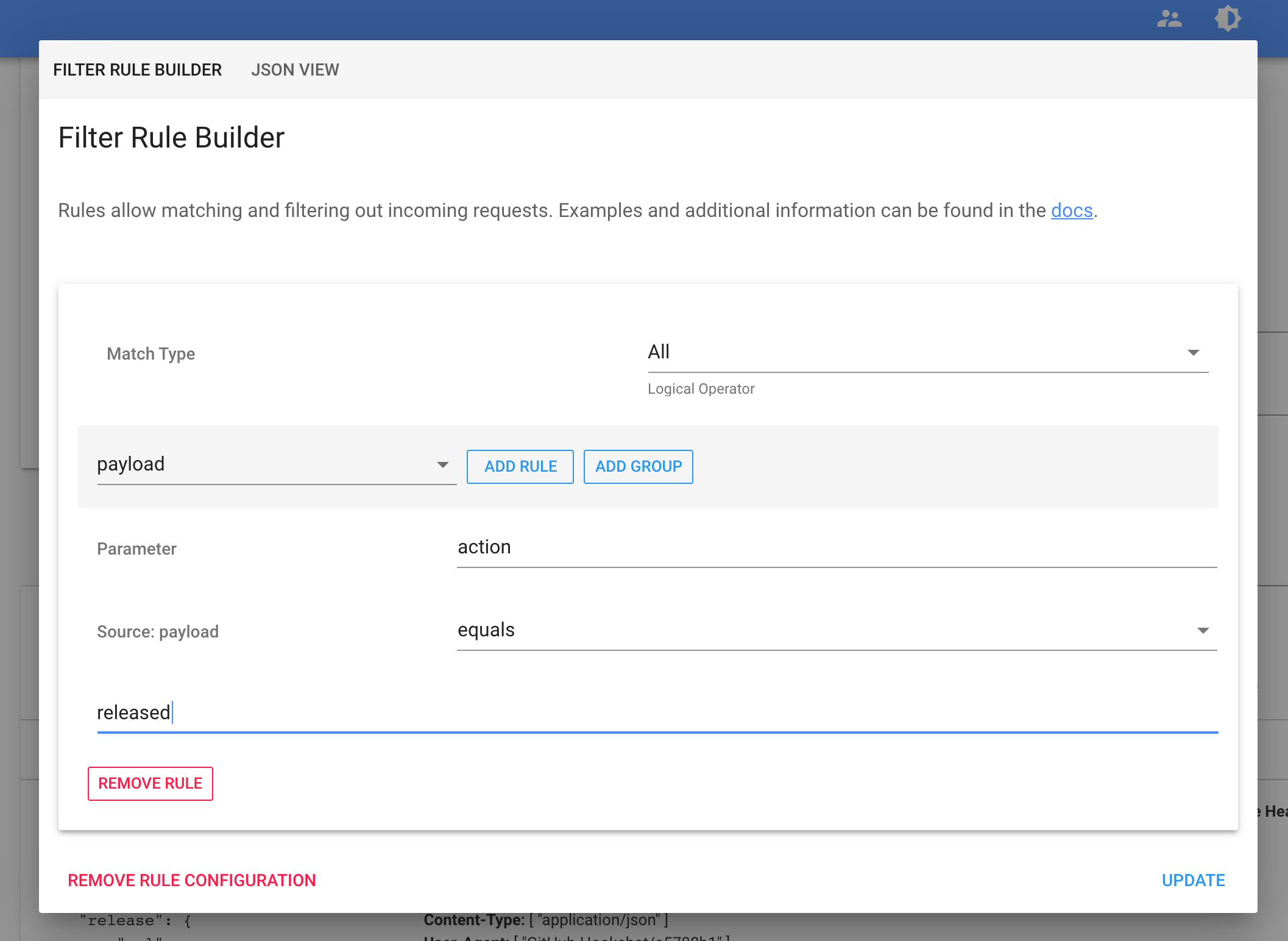
Now, go to your repository's releases page (for example https://github.com/webhookrelay/docker-compose-update-on-git-push/releases) and make a new release 1.0.0. Then, if you visit bucket details page or logs page - you should see webhook from Github. Open it and let's inspect the payload. It's quite lengthy but we should be able to see
"action": "released",
in the top. To ensure that we only react on these events, create a rule:
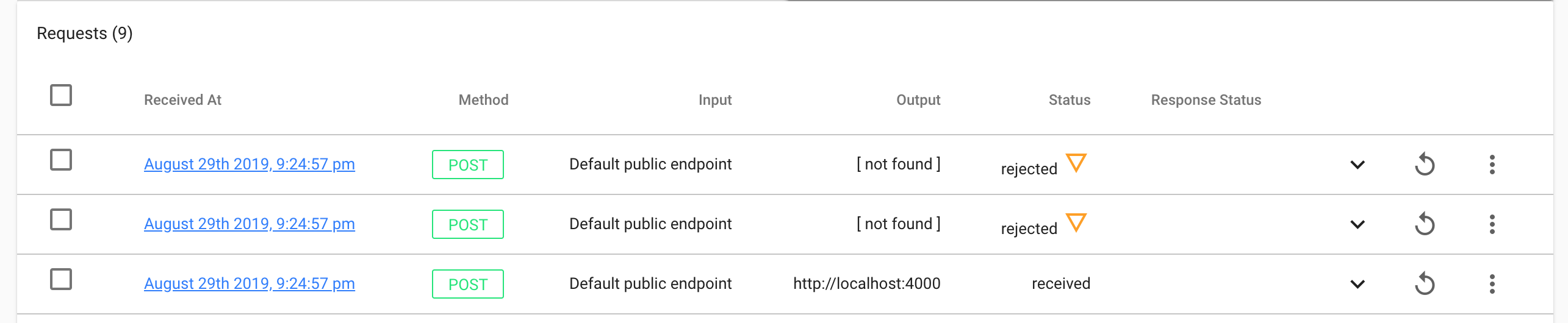
If you tag another release, you should see now that only one webhook was forwarder
Step 3: Update script and starting relay background service
Our update script is:
#!/bin/bash
git pull
docker-compose up -d
It will pull the latest compose file and update containers. Now, let's update configuration in relay.yml file (access key & secret can be generated here):
version: v1
key: xxx # your access key
secret: xxx # your access secret
buckets:
- docker-compose-update-on-git-push # your bucket name where github webhooks are sent
relayer:
type: exec
command: bash
commandArgs:
- /full/path/to/docker-compose-update-on-git-push/update.sh # <-- should be full path to your update script
timeout: 300
To start the relay, run:
relay run -c relay.yml
This will be running it through your terminal. For production use cases, please use background service mode. It will ensure that the daemon is launched on OS startup.
Let's try it out
Launch docker-compose:
docker-compose up -d
Check containers:
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
26cd2219e18b redis:alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 20 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 6379/tcp docker-compose-update-on-git-push_redis_1
63c8cd1ae7bb karolisr/python-counter:0.1.0 "flask run" 20 seconds ago Up 18 seconds 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp docker-compose-update-on-git-push_web_1
$ curl http://localhost:5000
I have been seen 1 times.
$ curl http://localhost:5000
I have been seen 2 times.
Next step would be to build a new image 0.2.0 and push it to the registry. Once it's available, we can update our github repository docker-compose.yml and make a new release. For the sake of this example, let's do this through the Github UI.
In a few seconds you should see a new container running:
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
27b2542423ec karolisr/python-counter:0.2.0 "flask run" 9 seconds ago Up 7 seconds 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp docker-compose-update-on-git-push_web_1
26cd2219e18b redis:alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 10 minutes ago Up 9 minutes 6379/tcp docker-compose-update-on-git-push_redis_1
Optional: Validating Github secret
Webhook Relay output rules can also validate Github signature:
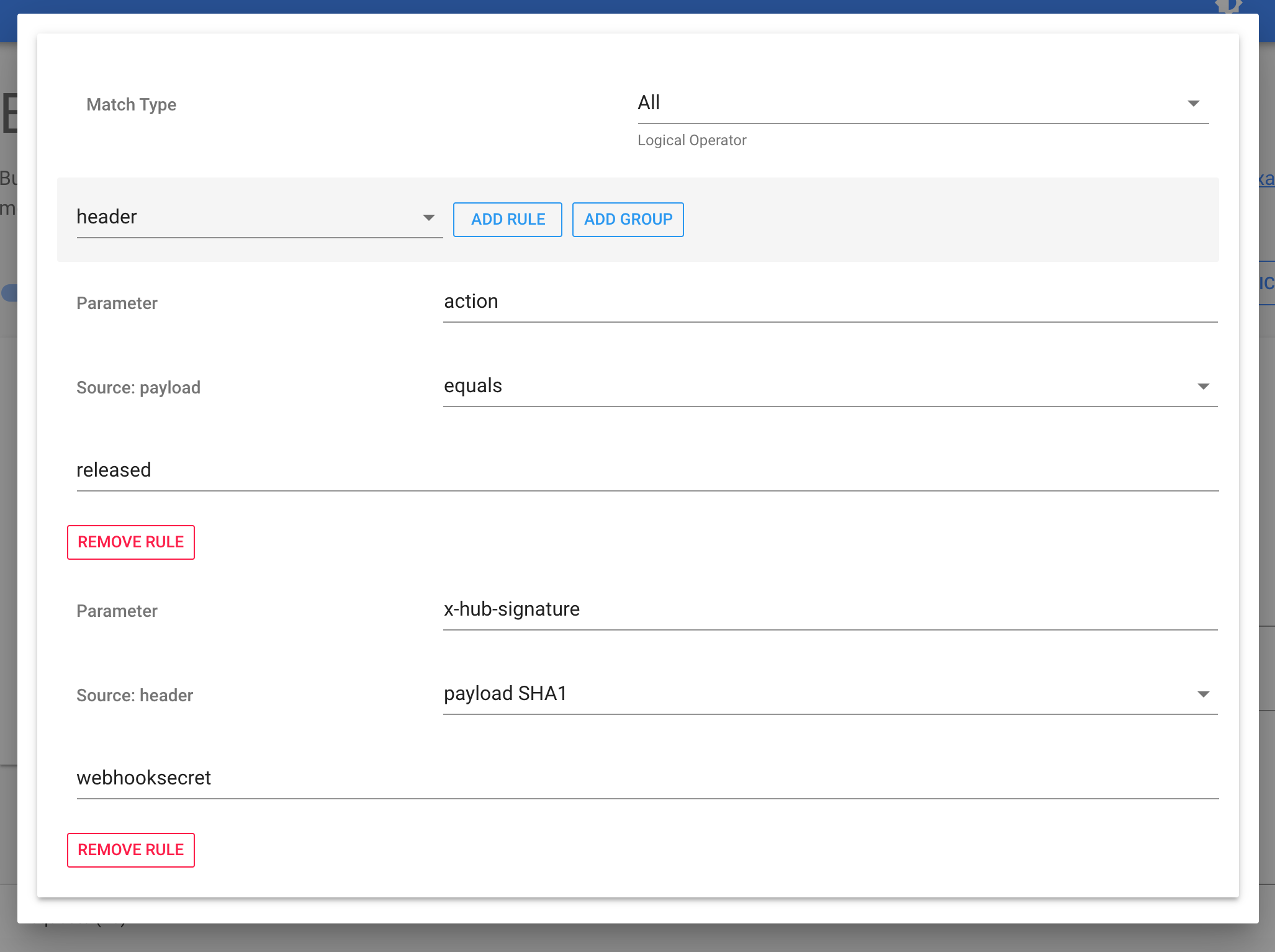
This will ensure that only webhooks signed by Github will be processed.
Conclusion
As with any code executed on your machine - you have to be careful when automating tasks. Webhook Relay will provide you with a unidirectional flow of webhooks into the machine. Your script/applications are on your machine and cannot be modified remotely through Webhook Relay. Coupled with authenticated webhook endpoints (you can configure it on a bucket level) or webhook payload checksum validation - you can build a secure update mechanism.
In general this is an easy way and simple way to update Docker Compose on your server without investing time. You can just push Docker images, update the tag and relay agent will run the update.

